
|
|
PDF ADSP-21020 Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | ADSP-21020 | |
| Descripción | 32/40-Bit IEEE Floating-Point DSP Microprocessor | |
| Fabricantes | Analog Devices | |
| Logotipo |  |
|
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de ADSP-21020 (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 30 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
www.DataSheet4U.com
a
32/40-Bit IEEE Floating-Point
DSP Microprocessor
ADSP-21020
FEATURES
Superscalar IEEE Floating-Point Processor
Off-Chip Harvard Architecture Maximizes Signal
Processing Performance
30 ns, 33.3 MIPS Instruction Rate, Single-Cycle
Execution
100 MFLOPS Peak, 66 MFLOPS Sustained Performance
1024-Point Complex FFT Benchmark: 0.58 ms
Divide (y/x): 180 ns
Inverse Square Root (1/√x): 270 ns
32-Bit Single-Precision and 40-Bit Extended-Precision
IEEE Floating-Point Data Formats
32-Bit Fixed-Point Formats, Integer and Fractional,
with 80-Bit Accumulators
IEEE Exception Handling with Interrupt on Exception
Three Independent Computation Units: Multiplier,
ALU, and Barrel Shifter
Dual Data Address Generators with Indirect, Immedi-
ate, Modulo, and Bit Reverse Addressing Modes
Two Off-Chip Memory Transfers in Parallel with
Instruction Fetch and Single-Cycle Multiply & ALU
Operations
Multiply with Add & Subtract for FFT Butterfly
Computation
Efficient Program Sequencing with Zero-Overhead
Looping: Single-Cycle Loop Setup
Single-Cycle Register File Context Switch
15 (or 25) ns External RAM Access Time for Zero-Wait-
State, 30 (or 40) ns Instruction Execution
IEEE JTAG Standard 1149.1 Test Access Port and
On-Chip Emulation Circuitry
223-Pin PGA Package (Ceramic)
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ADSP-21020 is the first member of Analog Devices’ family
of single-chip IEEE floating-point processors optimized for
digital signal processing applications. Its architecture is similar
to that of Analog Devices’ ADSP-2100 family of fixed-point
DSP processors.
Fabricated in a high-speed, low-power CMOS process, the
ADSP-21020 has a 30 ns instruction cycle time. With a high-
performance on-chip instruction cache, the ADSP-21020 can
execute every instruction in a single cycle.
The ADSP-21020 features:
• Independent Parallel Computation Units
The arithmetic/logic unit (ALU), multiplier and shifter
perform single-cycle instructions. The units are architecturally
arranged in parallel, maximizing computational throughput. A
single multifunction instruction executes parallel ALU and
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
DATA ADDRESS
GENERATORS
DAG 1 DAG 2
INSTRUCTION
CACHE
PROGRAM
SEQUENCER
JTAG TEST
& EMULATION
PROGRAM MEMORY ADDRESS
DATA MEMORY ADDRESS
PROGRAM MEMORY DATA
DATA MEMORY DATA
REGISTER FILE
TIMER
EXTERNAL
ADDRESS
BUSES
EXTERNAL
DATA
BUSES
ALU
ARITHMETIC UNITS
MULTIPLIER
SHIFTER
multiplier operations. These computation units support IEEE
32-bit single-precision floating-point, extended precision
40-bit floating-point, and 32-bit fixed-point data formats.
• Data Register File
A general-purpose data register file is used for transferring
data between the computation units and the data buses, and
for storing intermediate results. This 10-port (16-register)
register file, combined with the ADSP-21020’s Harvard
architecture, allows unconstrained data flow between
computation units and off-chip memory.
• Single-Cycle Fetch of Instruction and Two Operands
The ADSP-21020 uses a modified Harvard architecture in
which data memory stores data and program memory stores
both instructions and data. Because of its separate program
and data memory buses and on-chip instruction cache, the
processor can simultaneously fetch an operand from data
memory, an operand from program memory, and an
instruction from the cache, all in a single cycle.
• Memory Interface
Addressing of external memory devices by the ADSP-21020 is
facilitated by on-chip decoding of high-order address lines to
generate memory bank select signals. Separate control lines
are also generated for simplified addressing of page-mode
DRAM.
The ADSP-21020 provides programmable memory wait
states, and external memory acknowledge controls allow
interfacing to peripheral devices with variable access times.
REV. C
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 617/329-4700
Fax: 617/326-8703
1 page 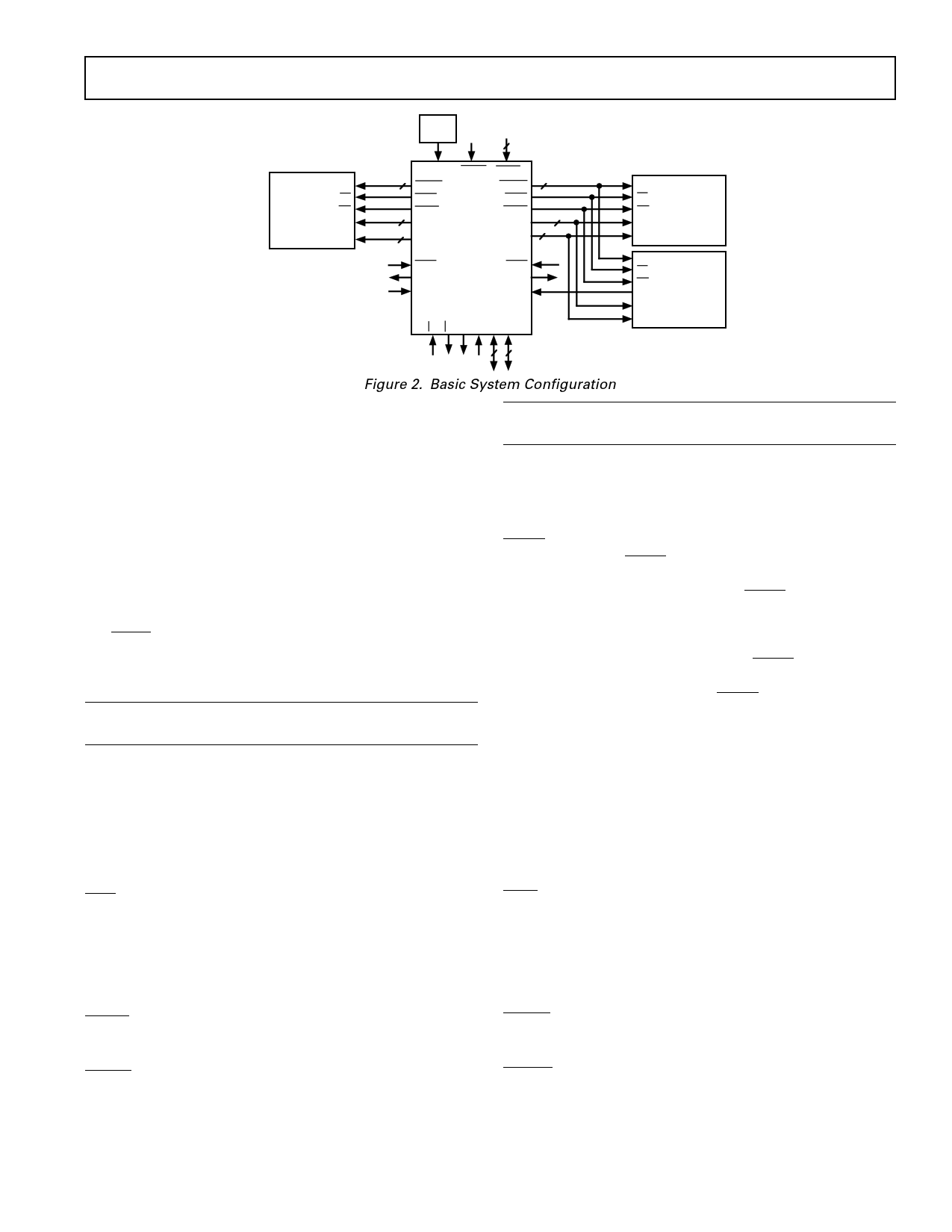
ADSP-21020
SELECTS
PROGRAM
MEMORY
OE
WE
ADDR
DATA
1×
CLOCK
4
CLKIN RESET IRQ3-0
2
PMS1-0
DMS3-0 4
PMRD
DMRD
24 PMWR
DMWR
PMA
48
PMD
DMA
32
DMD
ADSP-21010
32
PMTS
PMPAGE
PMACK
DMTS
DMPAGE
DMACK
SELECTS
OE
WE
ADDR
DATA
MEMORY
DATA
SELECTS
OE
WE
ACK
PERIPHERALS
ADDR
DATA
45
Figure 2. Basic System Configuration
The ADSP-21020 also implements on-chip emulation through
the JTAG test access port. The processor’s eight sets of break-
point range registers enable program execution at full speed
until reaching a desired break-point address range. The
processor can then halt and allow reading/writing of all the
processor’s internal registers and external memories through the
JTAG port.
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
This section describes the pins of the ADSP-21020. When
groups of pins are identified with subscripts, e.g. PMD47–0, the
highest numbered pin is the MSB (in this case, PMD47). Inputs
identified as synchronous (S) must meet timing requirements
with respect to CLKIN (or with respect to TCK for TMS, TDI,
and TRST). Those that are asynchronous (A) can be asserted
asynchronously to CLKIN.
O = Output; I = Input; S = Synchronous; A = Asynchronous;
P = Power Supply; G = Ground.
Pin
Name Type Function
PMA23–0 O
PMD47–0 I/O
PMS1–0 O
PMRD O
PMWR O
PMACK I/S
Program Memory Address. The ADSP-21020
outputs an address in program memory on
these pins.
Program Memory Data. The ADSP-21020
inputs and outputs data and instructions on
these pins. 32-bit fixed-point data and 32-bit
single-precision floating-point data is trans-
ferred over bits 47-16 of the PMD bus.
Program Memory Select lines. These pins are
asserted as chip selects for the corresponding
banks of program memory. Memory banks
must be defined in the memory control
registers. These pins are decoded program
memory address lines and provide an early
indication of a possible bus cycle.
Program Memory Read strobe. This pin is
asserted when the ADSP-21020 reads from
program memory.
Program Memory Write strobe. This pin is
asserted when the ADSP-21020 writes to
program memory.
Program Memory Acknowledge. An external
device deasserts this input to add wait states
to a memory access.
Pin
Name
Type Function
PMPAGE O
PMTS I/S
DMA31–0 O
DMD39–0 I/O
DMS3–0 O
DMRD O
DMWR O
DMACK I/S
Program Memory Page Boundary. The
ADSP-21020 asserts this pin to signal that a
program memory page boundary has been
crossed. Memory pages must be defined in
the memory control registers.
Program Memory Three-State Control.
PMTS places the program memory address,
data, selects, and strobes in a high-
impedance state. If PMTS is asserted while
a PM access is occurring, the processor will
halt and the memory access will not be
completed. PMACK must be asserted for at
least one cycle when PMTS is deasserted to
allow any pending memory access to com-
plete properly. PMTS should only be
asserted (low) during an active memory
access cycle.
Data Memory Address. The ADSP-21020
outputs an address in data memory on these
pins.
Data Memory Data. The ADSP-21020
inputs and outputs data on these pins.
32-bit fixed point data and 32-bit
single-precision floating point data is
transferred over bits 39-8 of the DMD bus.
Data Memory Select lines. These pins are
asserted as chip selects for the correspon-
ding banks of data memory. Memory banks
must be defined in the memory control
registers. These pins are decoded data
memory address lines and provide an early
indication of a possible bus cycle.
Data Memory Read strobe. This pin is
asserted when the ADSP-21020 reads from
data memory.
Data Memory Write strobe. This pin is
asserted when the ADSP-21020 writes to
data memory.
Data Memory Acknowledge. An external
device deasserts this input to add wait states
to a memory access.
REV. C
–5–
5 Page 
Table Vll. Multifunction Compute Operations
Fixed-Point
Rm=R3-0 * R7-4 (SSFR), Ra=R11-8 + R15-12
Rm=R3-0 * R7-4 (SSFR), Ra=R11-8 – R15-12
Rm=R3-0 * R7-4 (SSFR), Ra=(R11-8 + R15-12)/2
MRF=MRF + R3-0 * R7-4 (SSF), Ra=R11-8 + R15-12
MRF=MRF + R3-0 * R7-4 (SSF), Ra=R11-8 – R15-12
MRF=MRF + R3-0 * R7-4 (SSF), Ra=(R11-8 + R15-12)/2
Rm=MRF + R3-0 * R7-4 (SSFR), Ra=R11-8 + R15-12
Rm=MRF + R3-0 * R7-4 (SSFR), Ra=R11-8 – R15-12
Rm=MRF + R3-0 * R7-4 (SSFR), Ra=(R11-8 + R15-12)/2
MRF=MRF – R3-0 * R7-4 (SSF), Ra=R11-8 + R15-12
MRF=MRF – R3-0 * R7-4 (SSF), Ra=R11-8 – R15-12
MRF=MRF – R3-0 * R7-4 (SSF), Ra=(R11-8 + R15-12)/2
Rm=MRF – R3-0 * R7-4 (SSFR), Ra=R11-8 + R15-12
Rm=MRF – R3-0 * R7-4 (SSFR), Ra=R11-8 – R15-12
Rm=MRF – R3-0 * R7-4 (SSFR), Ra=(R11-8 + R15-12)/2
Rm=R3-0 * R7-4 (SSFR), Ra=R11-8 + R15-12,
Rs=R11-8 – R15-12
Floating-Point
Fm=F3-0 * F7-4, Fa=F11-8 + F15-12
Fm=F3-0 * F7-4, Fa=F11-8 – F15-12
Fm=F3-0 * F7-4, Fa=FLOAT R11-8 by R15-12
Fm=F3-0 * F7-4, Fa=FIX R11-8 by R15-12
Fm=F3-0 * F7-4, Fa=(F11-8 + F15-12)/2
Fm=F3-0 * F7-4, Fa=ABS F11-8
Fm=F3-0 * F7-4, Fa=MAX (F11-8, F15-12)
Fm=F3-0 * F7-4, Fa=MIN (F11-8, F15-12)
Fm=F3-0 * F7-4, Fa=F11-8 + F15-12,
Fs=F11-8 – F15-12
Ra, Rm
R3-0
R7-4
R11-8
R15-12
Fa, Fm
F3-0
F7-4
F11-8
F15-12
(SSF)
(SSFR)
Any register file location (fixed-point)
R3, R2, R1, R0
R7, R6, R5, R4
R11, R10, R9, R8
R15, R14, R13, R12
Any register file location (floating-point)
F3, F2, F1, F0
F7, F6, F5, F4
F11, F10, F9, F8
F15, F14, F13, F12
X-input signed, Y-input signed, fractional inputs
X-input signed, Y-input signed, fractional inputs, rounded output
ADSP-21020
Table VIII. Interrupt Vector Addresses and Priorities
Vector
Address
No. (Hex)
Function
0
1*
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19–23
24–31
0x00
0x08
0xl0
0xl8
0x20
0x28
0x30
0x38
0x40
0x48
0x50
0x58
0x60
0x68
0x70
0x78
0x80
0x88
0x90
0x98-0xB8
0xC0–OxF8
Reserved
Reset
Reserved
Status stack or loop stack overflow or
PC stack full
Timer=0 (high priority option)
IRQ3 asserted
IRQ2 asserted
IRQ1 asserted
IRQ0 asserted
Reserved
Reserved
DAG 1 circular buffer 7 overflow
DAG 2 circular buffer 15 overflow
Reserved
Timer=0 (low priority option)
Fixed-point overflow
Floating-point overflow
Floating-point underflow
Floating-point invalid operation
Reserved
User software interrupts
*Nonmaskable
REV. C
–11–
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 30 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet ADSP-21020.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| ADSP-21020 | 32/40-Bit IEEE Floating-Point DSP Microprocessor | Analog Devices |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
