
|
|
PDF 80C286 Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | 80C286 | |
| Descripción | High Performance Microprocessor | |
| Fabricantes | Intersil Corporation | |
| Logotipo |  |
|
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de 80C286 (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 30 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
® 80C286
January 28, 2008
High Performance Microprocessor
with Memory Management and Protection
Features
• Compatible with NMOS 80286
• Wide Range of Clock Rates
- DC to 25MHz (80C286-25)
- DC to 20MHz (80C286-20)
- DC to 16MHz (80C286-16)
- DC to 12.5MHz (80C286-12)
- DC to 10MHz (80C286-10)
• Static CMOS Design for Low Power Operation
- ICCSB = 5mA Maximum
- ICCOP = 185mA Maximum (80C286-10)
220mA Maximum (80C286-12)
260mA Maximum (80C286-16)
310mA Maximum (80C286-20)
410mA Maximum (80C286-25)
• High Performance Processor (Up to 19 Times the 8086
Throughput)
• Large Address Space
• 16 Megabytes Physical/1 Gigabyte Virtual per Task
• Integrated Memory Management, Four-Level Memory
Protection and Support for Virtual Memory and Operat-
ing Systems
• Two 80C86 Upward Compatible Operating Modes
- 80C286 Real Address Mode
- PVAM
• Compatible with 80287 Numeric Data Co-Processor
• High Bandwidth Bus Interface (25 Megabyte/Sec)
• Available In
- 68 Pin PGA (Commercial, Industrial, and Military)
- 68 Pin PLCC (Commercial and Industrial)
Description
The Intersil 80C286 is a static CMOS version of the NMOS
80286 microprocessor. The 80C286 is an advanced, high-
performance microprocessor with specially optimized capa-
bilities for multiple user and multi-tasking systems. The
80C286 has built-in memory protection that supports operat-
ing system and task isolation as well as program and data
privacy within tasks. A 25MHz 80C286 provides up to nine-
teen times the throughput of a standard 5MHz 8086. The
80C286 includes memory management capabilities that map
230 (one gigabyte) of virtual address space per task into 224
bytes (16 megabytes) of physical memory.
The 80C286 is upwardly compatible with 80C86 and 80C88
software (the 80C286 instruction set is a superset of the
80C86/80C88 instruction set). Using the 80C286 real
address mode, the 80C286 is object code compatible with
existing 80C86 and 80C88 software. In protected virtual
address mode, the 80C286 is source code compatible with
80C86 and 80C88 software but may require upgrading to
use virtual address as supported by the 80C286’s integrated
memory management and protection mechanism. Both
modes operate at full 80C286 performance and execute a
superset of the 80C86 and 80C88 instructions.
The 80C286 provides special operations to support the effi-
cient implementation and execution of operating systems.
For example, one instruction can end execution of one task,
save its state, switch to a new task, load its state, and start
execution of the new task. The 80C286 also supports virtual
memory systems by providing a segment-not-present excep-
tion and restartable instructions.
Ordering Information
PACKAGE
PGA
PLCC
TEMP. RANGE
0oC to +70oC
-40oC to +85oC
-55oC to +125oC
0oC to +70oC
-40oC to +85oC
10MHz
-
IG80C286-10
5962-
9067801MXC
-
IS80C286-10
12.5MHz
CG80C286-12
IG80C286-12
5962-
9067802MXC
CS80C286-12
IS80C286-12
16MHz
CG80C286-16
-
-
CS80C286-16
IS80C286-16
20MHz
CG80C286-20
-
-
CS80C286-20
IS80C286-20
25MHz
-
-
-
CS80C286-25
-
PKG. NO.
G68.B
G68.B
G68.B
N68.95
N68.95
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
1-888-INTERSIL or 1-888-468-3774 | Intersil (and design) is a registered trademark of Intersil Americas Inc.
Copyright © Intersil Americas Inc. 2003-2008. All Rights Reserved
All other trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners.
1
FN2947.3
1 page 
80C286
Pin Descriptions The following pin function descriptions are for the 80C286 microprocessor. (Continued)
PIN
SYMBOL NUMBER
TYPE
DESCRIPTION
M / IO
67
O MEMORY I/O SELECT: distinguishes memory access from I/O access. If HIGH during TS, a mem-
ory cycle or a halt/shutdown cycle is in progress. If LOW, an I/O cycle or an interrupt acknowledge
cycle is in progress. M/IO is held at high impedance to the last valid logic state during bus hold ac-
knowledge.
COD / lNTA
66
LOCK
68
O CODE/INTERRUPT ACKNOWLEDGE: distinguishes instruction fetch cycles from memory data
read cycles. Also distinguishes interrupt acknowledge cycles from I/O cycles. COD/lNTA is held at
high impedance to the last valid logic state during bus hold acknowledge. Its timing is the same as
M / IO.
O BUS LOCK: indicates that other system bus masters are not to gain control of the system bus for
the current and following bus cycles. The LOCK signal may be activated explicitly by the “LOCK”
instruction prefix or automatically by 80C286 hardware during memory XCHG instructions, interrupt
acknowledge, or descriptor table access. LOCK is active LOW and is held at a high impedance logic
one during bus hold acknowledge.
READY
63
HOLD
HLDA
64
65
INTR
57
NMI 59
PEREQ
PEACK
61
6
BUSY
ERROR
54
53
l BUS READY: terminates a bus cycle. Bus cycles are extended without limit until terminated by
READY LOW. READY is an active LOW synchronous input requiring setup and hold times relative
to the system clock be met for correct operation. READY is ignored during bus hold acknowledge.
(See Note 1)
I BUS HOLD REQUEST AND HOLD ACKNOWLEDGE: control ownership of the 80C286 local bus.
O The HOLD input allows another local bus master to request control of the local bus. When control is
granted, the 80C286 will float its bus drivers and then activate HLDA, thus entering the bus hold ac-
knowledge condition. The local bus will remain granted to the requesting master until HOLD be-
comes inactive which results in the 80C286 deactivating HLDA and regaining control of the local
bus. This terminates the bus hold acknowledge condition. HOLD may be asynchronous to the sys-
tem clock. These signals are active HIGH. Note that HLDA never floats.
I INTERRUPT REQUEST: requires the 80C286 to suspend its current program execution and service
a pending external request. Interrupt requests are masked whenever the interrupt enable bit in the
flag word is cleared. When the 80C286 responds to an interrupt request, it performs two interrupt
acknowledge bus cycles to read an 8-bit interrupt vector that identifies the source of the interrupt.
To ensure program interruption, INTR must remain active until an interrupt acknowledge bus cycle
is initiated. INTR is sampled at the beginning of each processor cycle and must be active HIGH at
least two processor cycles before the current instruction ends in order to interrupt before the next
instruction. INTR is level sensitive, active HIGH, and may be asynchronous to the system clock.
l NON-MASKABLE INTERRUPT REQUEST: interrupts the 80C286 with an internally supplied vector
value of two. No interrupt acknowledge cycles are performed. The interrupt enable bit in the 80C286
flag word does not affect this input. The NMI input is active HIGH, may be asynchronous to the sys-
tem clock, and is edge triggered after internal synchronization. For proper recognition, the input must
have been previously LOW for at least four system clock cycles and remain HIGH for at least four
system clock cycles.
l PROCESSOR EXTENSION OPERAND REQUEST AND ACKNOWLEDGE: extend the memory
O management and protection capabilities of the 80C286 to processor extensions. The PEREQ input
requests the 80C286 to perform a data operand transfer for a processor extension. The PEACK out-
put signals the processor extension when the requested operand is being transferred. PEREQ is ac-
tive HIGH. PEACK is active LOW and is held at a high impedance logic one during bus hold
acknowledge. PEREQ may be asynchronous to the system clock.
l PROCESSOR EXTENSION BUSY AND ERROR: indicates the operating condition of a processor
I extension to the 80C286. An active BUSY input stops 80C286 program execution on WAIT and
some ESC instructions until BUSY becomes inactive (HIGH). The 80C286 may be interrupted while
waiting for BUSY to become inactive. An active ERROR input causes the 80C286 to perform a pro-
cessor extension interrupt when executing WAIT or some ESC instructions. These inputs are active
LOW and may be asynchronous to the system clock.
5
5 Page 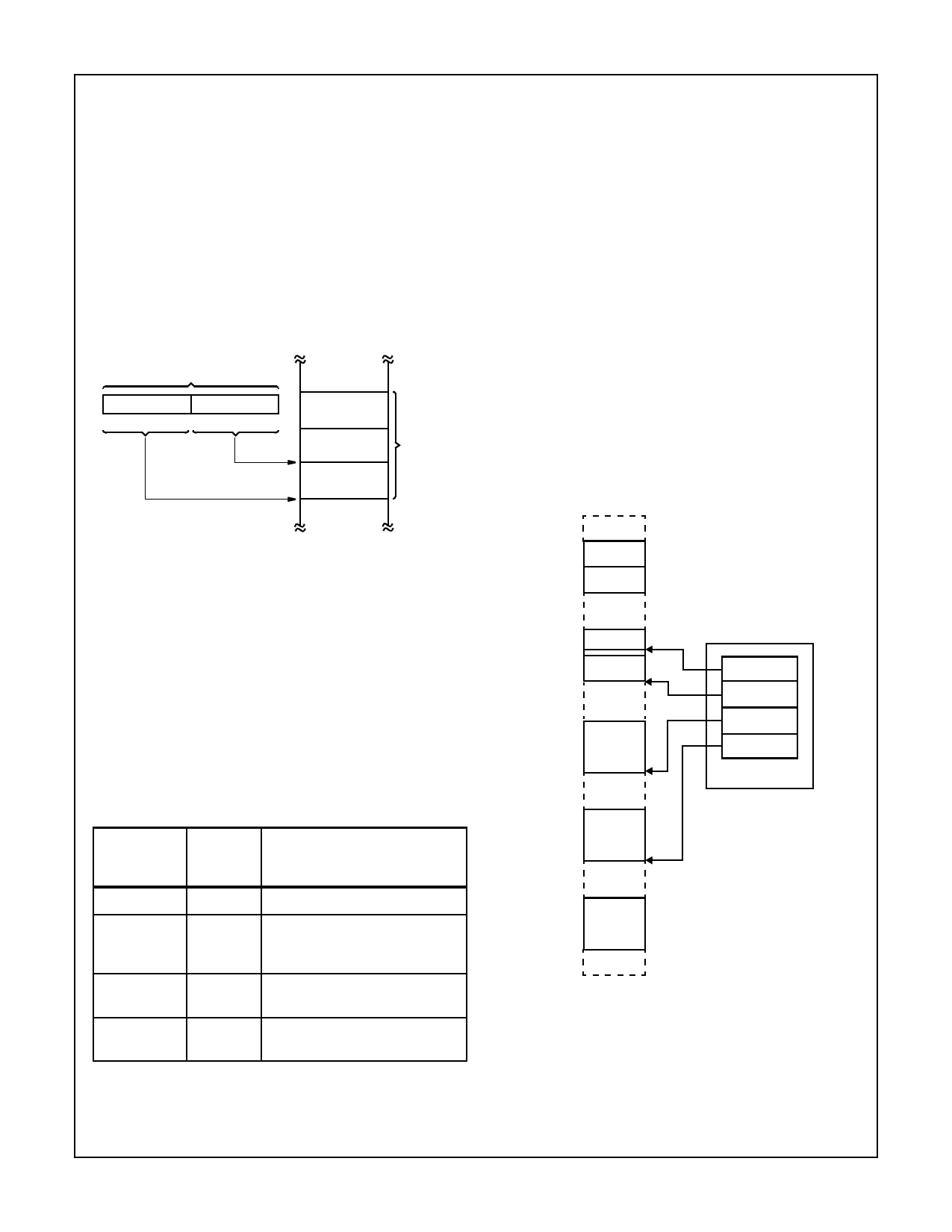
80C286
Memory Organization
Memory is organized as sets of variable-length segments. Each
segment is a linear contiguous sequence of up to 64K (216) 8-
bit bytes. Memory is addressed using a two-component
address (a pointer) that consists of a 16-bit segment selector
and a 16-bit offset. The segment selector indicates the desired
segment in memory. The offset component indicates the
desired byte address within the segment. (See Figure 3).
All instructions that address operands in memory must spec-
ify the segment and the offset. For speed and compact
instruction encoding, segment selectors are usually stored in
the high speed segment registers. An instruction need spec-
ify only the desired segment register and offset in order to
address a memory operand.
POINTER
SEGMENT
OFFSET
31 16 15
0
OPERAND
SELECTED
SELECTED
SEGMENT
Addressing Modes
The 80C286 provides a total of eight addressing modes for
instructions to specify operands. Two addressing modes are
provided for instructions that operate on register or immedi-
ate operands:
REGISTER OPERAND MODE: The operand is located in
one of the 8 or 16-bit general registers.
IMMEDIATE OPERAND MODE: The operand is included in
the instruction.
Six modes are provided to specify the location of an operand in
a memory segment. A memory operand address consists of
two 16-bit components: segment selector and offset. The seg-
ment selector is supplied by a segment register either implicitly
chosen by the addressing mode or explicitly chosen by a seg-
ment override prefix. The offset is calculated by summing any
combination of the following three address elements:
the displacement (an 8 or 16-bit immediate value contained
in the instruction)
the base (contents of either the BX or BP base registers)
the index (contents of either the SI or Dl index registers)
MEMORY
FIGURE 3. TWO COMPONENT ADDRESS
Most instructions need not explicitly specify which segment
register is used. The correct segment register is automati-
cally chosen according to the rules of Table 3. These rules
follow the way programs are written (see Figure 4) as inde-
pendent modules that require areas for code and data, a
stack, and access to external data areas.
Special segment override instruction prefixes allow the
implicit segment register selection rules to be overridden for
special cases. The stack, data and extra segments may
coincide for simple programs. To access operands not resid-
ing in one of the four immediately available segments, a full
32-bit pointer or a new segment selector must be loaded.
TABLE 3. SEGMENT REGISTER SELECTION RULES
MEMORY SEGMENT
REFERENCE REGISTER
NEEDED
USED
IMPLICIT SEGMENT
SELECTION RULE
MODULE A
CODE
DATA
MODULE B
CODE
DATA
PROCESS
STACK
PROCESS
DATA
BLOCK 1
CPU
CODE
DATA
STACK
EXTRA
SEGMENT
REGISTERS
Instructions
Stack
Code (CS) Automatic with instruction prefetch
Stack (SS) All stack pushes and pops. Any
memory reference which uses BP
as a base register.
PROCESS
DATA
BLOCK 2
Local Data
External
(Global) Data
Data (DS) All data references except when
relative to stack or string destination
Extra (ES) Alternate data segment and
destination of string operation
MEMORY
FIGURE 4. SEGMENTED MEMORY HELPS STRUCTURE
SOFTWARE
Any carry out from the 16-bit addition is ignored. Eight-bit
displacements are sign extended to 16-bit values.
11
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 30 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet 80C286.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| 80C286 | High Performance Microprocessor | Intersil Corporation |
| 80C286 | High Performance Microprocessor | Harris |
| 80C286-883 | 80C286/883 High Performance Microprocessor | Intersil |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
