
|
|
PDF AD9393 Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | AD9393 | |
| Descripción | Low Power HDMI Display Interface | |
| Fabricantes | Analog Devices | |
| Logotipo |  |
|
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de AD9393 (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 30 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
FEATURES
HDMI interface
Supports high bandwidth digital content protection
RGB to YCrCb 2-way color conversion
1.8 V/3.3 V power supply
76-ball BGA package
RGB and YCrCb output formats
Digital video interface
HDMI 1.2a, DVI 1.0
80 MHz HDMI receiver
Supports high bandwidth digital content protection
(HDCP 1.1)
Digital audio interface
HDMI 1.2a-compatible audio interface
S/PDIF (IEC60958-compatible) digital audio output
Multichannel I2S audio output (up to 8 channels)
APPLICATIONS
Portable low power TV
HDTV
Projectors
LCD monitor
Low Power HDMI Display Interface
AD9393
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
SCL
SDA
Rx0+
Rx0–
Rx1+
Rx1–
Rx2+
Rx2–
RxC+
RxC–
RTERM
SERIAL
REGISTER
AND
POWER
MANAGEMENT
R/G/B 8 × 3
OR YCrCb
HDMI
RECEIVER
DATACK
HSYNC
VSYNC
DE
MCL
MDA
DDC_SCL
DDC_SDA
HDCP
AD9393
Figure 1.
D[23:0]
DCLK
HSOUT
VSOUT
DE
SPDIF
8-CHANNEL
I2S
MCLK
SCLK
LRCLK
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9393 offers a High-Definition Multimedia Interface
(HDMI™) receiver integrated on a single chip. Support is also
included for high bandwidth digital content protection (HDCP).
The AD9393 contains a HDMI 1.2a-compatible receiver and
supports HDTV formats (up to 720p or 1080i) and displays
resolutions up to XGA (1024 × 768 @ 75 Hz). The receiver
features an intrapair skew tolerance of up to one full clock
cycle. With the inclusion of HDCP, displays may now receive
encrypted video content. The AD9393 allows for authentication
of a video receiver, decryption of encoded data at the receiver,
and renewability of that authentication during transmission as
specified by the HDCP 1.1 protocol.
Fabricated in an advanced CMOS process, the AD9393 is
provided in a space-saving 76-ball, surface-mount, Pb-free,
ball grid array (BGA) and is specified over the −10°C to
+80°C temperature range.
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarksandregisteredtrademarksarethepropertyoftheirrespectiveowners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113
©2009 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
1 page 
AD9393
DIGITAL INTERFACE ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
VDD = VD =3.3 V, DVDD = PVDD = 1.8 V, unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
Parameter
DC DIGITAL I/O Specifications
High-Level Input Voltage (VIH)
Low-Level Input Voltage (VIL)
High-Level Output Voltage (VOH)
Low-Level Output Voltage (VOL)
DC SPECIFICATIONS
Output High Level
IOHD (VOUT = VOH)
Output Low Level
IOLD (VOUT = VOL)
DCLK High Level
VOHC (VOUT = VOH)
DCLK Low Level
VOLC (VOUT = VOL)
Differential Input Voltage, Single-Ended Amplitude
POWER SUPPLY
VD
VDD
DVDD
PVDD
Power—54 MHz, YCrCb 422, CSC Disabled
Supply Current (Worst Pattern)1
IVD
IVDD
I2
DVDD
IPVDD
Power—74.25 MHz, RGB, CSC Disabled
Supply Current (Worst Pattern)1
IVD
IVDD
IDVDD
IPVDD
Power-Down Power
AC SPECIFICATIONS
Intrapair (+ to −) Differential Input Skew (tDPS)
Channel-to-Channel Differential Input Skew (tCCS)
Low-to-High Transition Time for Data and Controls (DLHT)
Low-to-High Transition Time for DCLK (DLHT)
High-to-Low Transition Time for Data and Controls (DHLT)
High-to-Low Transition Time for DCLK (DHLT)
Clock-to-Data Skew3 (tSKEW)
Duty Cycle, DCLK3
DCLK Frequency (fCIP)
Test
Level Conditions
VI
VI
VI
VI
IV Output drive = high strength
IV Output drive = low strength
IV Output drive = high strength
IV Output drive = low strength
IV Output drive = high strength
IV Output drive = low strength
IV Output drive = high strength
IV Output drive = low
IV
IV
IV
IV
IV
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
VI
IV
IV
IV Output drive = high; CL = 10 pF
IV Output drive = low; CL = 5 pF
IV Output drive = high; CL = 10 pF
IV Output drive = low; CL = 5 pF
IV Output drive = high; CL = 10 pF
IV Output drive = low; CL = 5 pF
IV Output drive = high; CL = 10 pF
IV Output drive = low; CL = 5 pF
IV
IV
VI
1 Worst-case pattern is alternating black and white pixels.
2 DCLK load = 10 pF, data load = 5 pF.
3 Drive strength = high.
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 40
Min Typ Max Unit
2.5
VDD − 0.1
VDD − 0.1
V
0.8 V
V
0.1 V
36 mA
24 mA
12 mA
8 mA
40 mA
20 mA
30 mA
15 mA
75 700 mV
3.15 3.3 3.47 V
1.7 3.3 347 V
1.7 1.8 1.9 V
1.7 1.8 1.9 V
485 mW
95 mA
18 mA
51 mA
26 mA
593 mW
109 mA
38 mA
66 mA
26 mA
130 mW
0.4 tBIT
0.6 tPIXEL
1000
ps
ps
1000
ps
ps
1000
ps
ps
1000
ps
ps
−0.5 +2.0 ns
45 50
%
20 80 MHz
5 Page 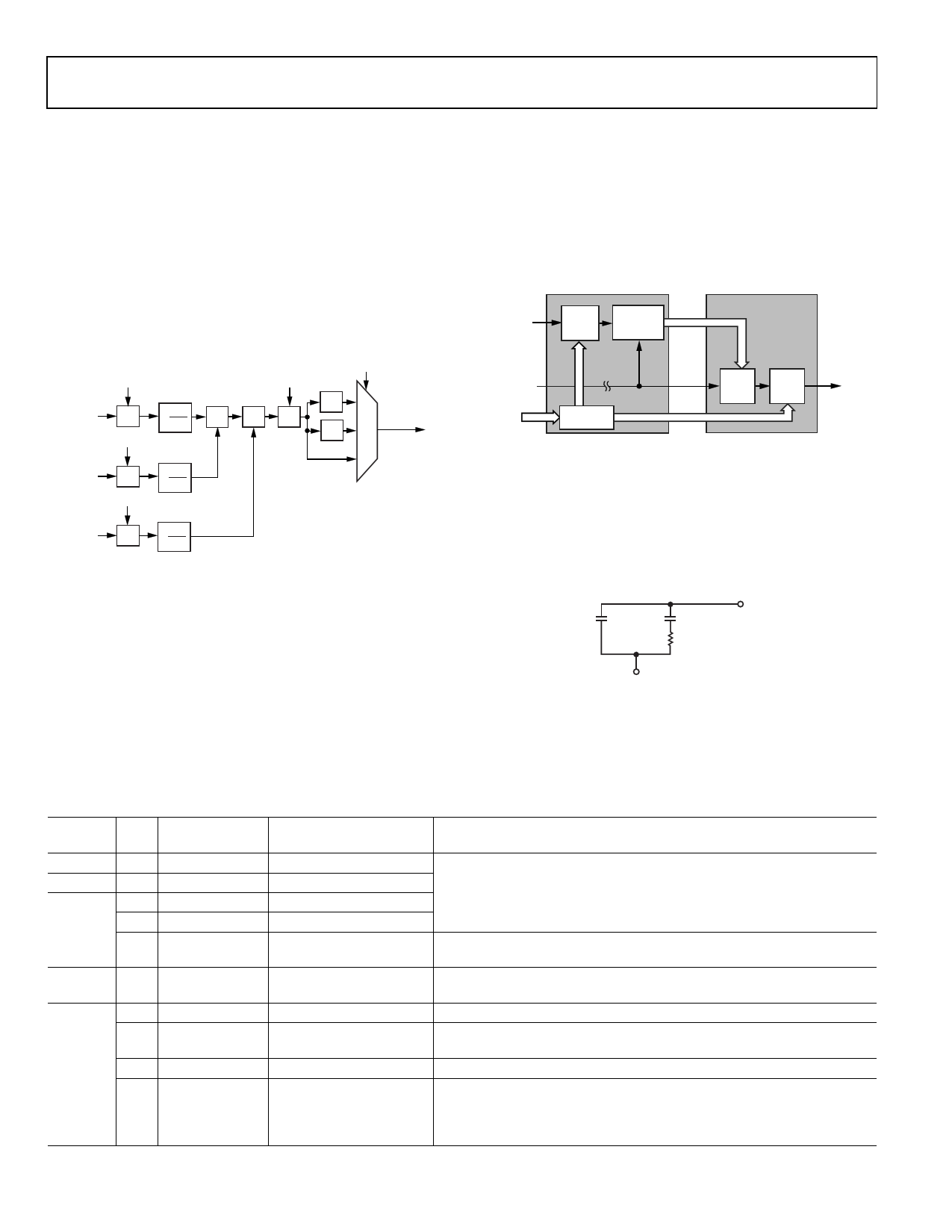
AD9393
One of the three input channels is represented in Figure 4.
In each processing channel, the three inputs are multiplied
by three separate coefficients marked a1, a2, and a3. These
coefficients are divided by 4096 to obtain nominal values
ranging from −0.9998 to +0.9998. The variable labeled a4 is
used as an offset control. The CSC_MODE setting is the same
for all three processing channels. This multiplies all coefficients
and offsets by a factor of 2 .CSC_MODE
audio, but also the sampling frequency (fS). The audio info-
frame also contains information about the N and CTS values
used to recreate the clock. With this information, it is possible
to regenerate the audio sampling frequency. The audio clock is
regenerated by dividing the 20-bit CTS value into the TMDS
clock, then multiplying by the 20-bit N value. This yields a
multiple of the sampling frequency of either 128 × fS or 256 ×
fS. It is possible for this to be specified up to 1024 × fS.
The functional diagram for a single channel of the CSC (as
shown in Figure 4) is repeated for the remaining G and B
channels. The coefficients for these channels are b1, b2, b3,
b4, c1, c2, c3, and c4.
a1[12:0]
a4[12:0]
CSC_MODE[1:0]
RIN[11:0]
×
×
1
4096
+
++
a2[12:0]
GIN[11:0]
×
×
1
4096
×4 2
ROUT[11:0]
×2 1
0
a3[12:0]
BIN[11:0]
×
×
1
4096
Figure 4. Single CSC Channel
A programming example and register settings for several
common conversions are listed in the Color Space Converter
(CSC) Common Settings section.
For a detailed functional description and more programming
examples that are compatible with the AD9393, refer to the
AN-795 Application Note, AD9880 Color Space Converter
User's Guide.
AUDIO PLL SETUP
Data contained in the audio infoframes (among other registers)
defines for the AD9393 HDMI receiver not only the type of
128 × fS
SOURCE DEVICE
DIVIDE
BY
N
CYCLE
TIME
COUNTER
CTS*
SINK DEVICE
VIDEO
CLOCK
N
REGISTER
N
TMDS
CLOCK
N*
÷ CTS
128 × fS
×N
*N AND CTS VALUES ARE TRANSMITTED USING THE
AUDIO CLOCK REGENERATION PACKET. VIDEO
CLOCK IS TRANSMITTED ON TMDS CLOCK CHANNEL.
Figure 5. N and CTS for Audio Clock
To provide the most flexibility in configuring the audio
sampling clock, an additional PLL is employed. The PLL
characteristics are determined by the loop filter design (see
Figure 6), the PLL charge pump current, and the VCO range
setting.
CP CZ PVDD
8nF 80nF
RZ
1.5kΩ
FILT
Figure 6. PLL Loop Filter Detail
To fully support all audio modes for all video resolutions up
to 1080i, it is necessary to adjust certain audio-related registers
from their power-on default values. Table 7 describes these
registers and gives the recommended settings.
Table 7. Audio Register Settings
Recommended
Register Bits Setting
0x01
[7:0] 0x00
0x02
[7:4] 0x40
0x03
[7:6] 01
[5:3] 010
[2] 1
Function
PLL divisor (MSBs)
PLL divisor (LSBs)
VCO range
Charge pump current
PLL enable
0x34
0x58
[5:4] 11
[7] 1
[6:4] 001
Audio frequency mode
override
MCLK PLL enable
MCLK PLL divisor
[3] 0
[2:0] 0**
N/CTS disable
MCLK sampling
frequency
Comments
The video PLL is used for the audio clock circuit when in HDMI mode. This
is done automatically.
In HDMI mode, this bit enables a lower frequency to be used for audio
MCLK generation.
Allows the chip to determine the low frequency mode of the audio PLL.
This enables the analog PLL to be used for audio MCLK generation.
When the analog PLL is enabled for MCLK generation, another frequency
divider is provided; these bits set the divisor to 2.
The N and CTS values should always be enabled.
000 = 128 × fS
001 = 256 × fS
010 = 384 × fS
011 = 512 × fS
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 40
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 30 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet AD9393.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| AD9393 | Low Power HDMI Display Interface | Analog Devices |
| AD9394 | 5 V Charge Pump HDMI Tx Companion Chip | Analog Devices |
| AD9396 | Analog/DVI Dual-Display Interface | Analog Devices |
| AD9397 | DVI Display Interface | Analog Devices |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
